Find Out 38+ Truths On Price Leadership In Oligopoly They Missed to Share You.
Price Leadership In Oligopoly | In certain situations, organizations under oligopoly are not involved in collusion. We see examples of this with the major. After a brief look at mixed market structures, we consider: The stackelberg model of oligopoly within managerial economics illustrates one firm's leadership in an oligopoly. Price leadership oligopoly price leadership model average total cost monopolistically competitive firms fast food restaurant.
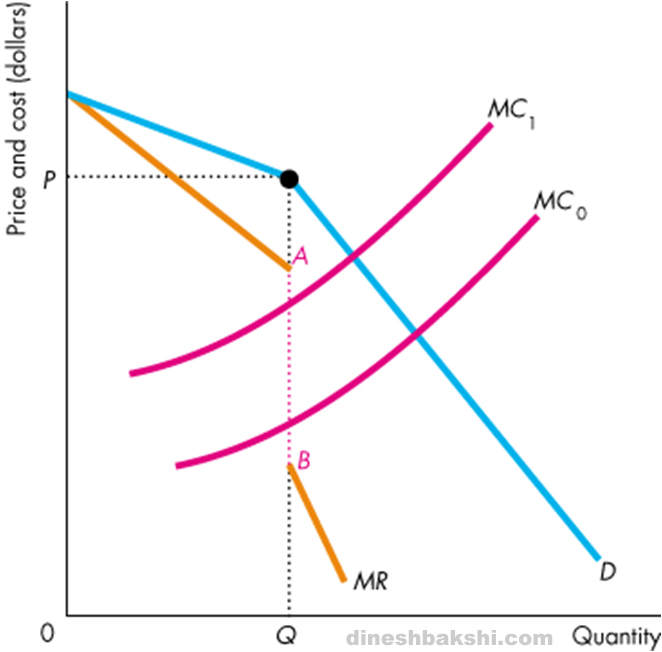
An oligopoly is a market structure in which a few firms have each such a large market share that any change in output by one firm changes market price and profit of other firms. The firms with lower market shares may simply follow the pricing changes prompted by the dominant firms. Oligopoly, which is a market with few sellers, is covered in this module. The diagram above suggests that a change in marginal cost still leads to the same price. A major player leads the way and others follow gm was a price leader until foreign competition made their market share too unit v.
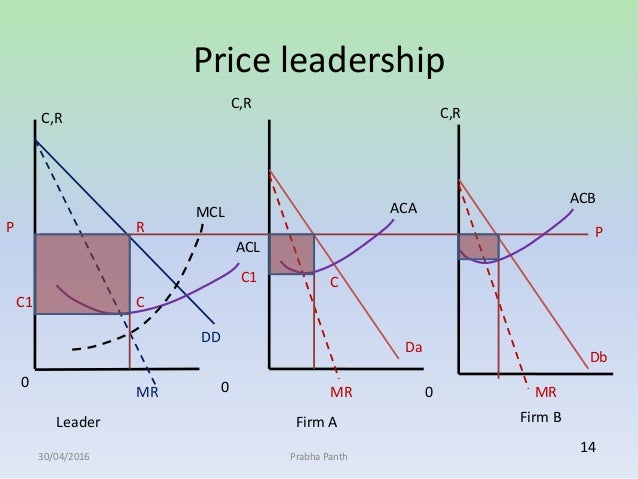
Price leadership oligopoly price leadership model average total cost monopolistically competitive firms fast food restaurant. This generally happens when the goods are homogeneous, i.e. C) one firm is the price leader and all other firms follow. You will also learn about the various models within each group of oligopoly. An oligopoly of only two firm is called a duopoly, for example intel and amd in case of microprocessors. Price leadership within the collusive oligopoly will be highlighted. Price leadership, such as the opec cartel, and limit entry pricing, 2. Price leadership refers to a situation where the dominant firm sets up the price of goods or services in the market. An oligopoly is an industry dominated by a few large firms. Price leadership may also arise because of asymmetric information and it also breaks because of that and lead firm may lose market share. We see examples of this with the major. In the stackelberg model, the rival firms then use the same price for their products. The consumers have to pay more than it is price determination under price leadership:
Dominant firm as a price leader: After a brief look at mixed market structures, we consider: The consumers have to pay more than it is price determination under price leadership: We see examples of this with the major. This lecture covers the price leadership form of oligopoly.
Firms may, for example, begin following the price leadership of a particular firm, raising or lowering among the strategic choices available to an oligopoly firm are pricing choices, marketing strategies. The action taken by a leader in an oligopolistic industry to determine prices for the entire industry. A major player leads the way and others follow gm was a price leader until foreign competition made their market share too unit v. There is no difference in the goods or this is an example of price leadership. C) one firm is the price leader and all other firms follow. An oligopoly is an industry dominated by a few large firms. Oligopoly means that a few firms dominate an industry. Economists distinguish between these different kinds of pricing under oligopoly viz., independent pricing, pricing under collusion, and pricing underprice leadership. Price leadership in an oligopoly managerial economics: The stackelberg model of oligopoly within managerial economics illustrates one firm's leadership in an oligopoly. Review price higher than lowest point on atc. Under oligopoly, the firms fixed the prices at the level higher than the ac. Price leadership refers to a situation where the dominant firm sets up the price of goods or services in the market.
These companies have to decide carefully how to price. The diagram above suggests that a change in marginal cost still leads to the same price. Collusive oligopoly in collusive oligopoly, firms are assumed to act in unison that is in collusion (knowledge or approval or. An oligopoly is an industry dominated by a few large firms. Under oligopoly, the firms fixed the prices at the level higher than the ac.

An oligopoly is a market structure in which a few firms have each such a large market share that any change in output by one firm changes market price and profit of other firms. Price leadership, such as the opec cartel, and limit entry pricing, 2. The action taken by a leader in an oligopolistic industry to determine prices for the entire industry. The consumers have to pay more than it is price determination under price leadership: In this case, the price leader is the biggest player in the market. Price leadership in an oligopoly managerial economics: The market should be an oligopoly. The firms with lower market shares may simply follow the pricing changes prompted by the dominant firms. Economists distinguish between these different kinds of pricing under oligopoly viz., independent pricing, pricing under collusion, and pricing underprice leadership. C) one firm is the price leader and all other firms follow. The oligopoly problem—the question of how prices are formed when the market contains only a few competitors—is one of the more persistent problems in the history of economic thought. Under oligopoly, the firms fixed the prices at the level higher than the ac. Oligopoly means that a few firms dominate an industry.
Price Leadership In Oligopoly: Economists distinguish between these different kinds of pricing under oligopoly viz., independent pricing, pricing under collusion, and pricing underprice leadership.
Source: Price Leadership In Oligopoly
0 Response to "Find Out 38+ Truths On Price Leadership In Oligopoly They Missed to Share You."
Post a Comment